Hydramnios (Polyhydramnios)
Comprehensive Nursing Notes for Evidence-Based Practice
Table of Contents
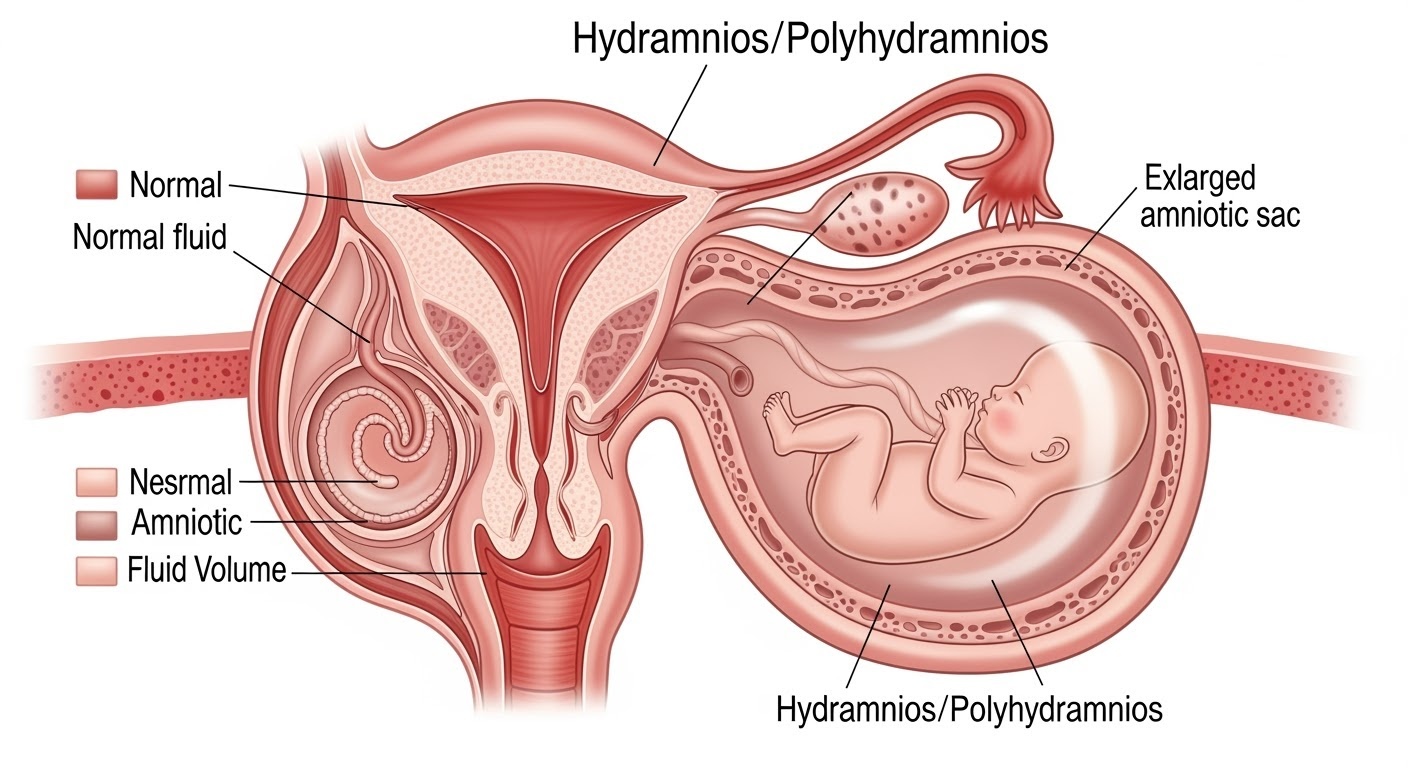
Figure 1: Cross-sectional view of hydramnios showing excessive amniotic fluid accumulation
Definition & Pathophysiology
What is Hydramnios?
Hydramnios, also known as polyhydramnios, is a pregnancy condition characterized by excessive accumulation of amniotic fluid in the amniotic sac. This condition occurs when amniotic fluid volume exceeds 2000mL (normal range: 500-1500mL) or when the Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI) is greater than 24cm.
The condition affects approximately 1-2% of all pregnancies and can lead to significant maternal and fetal complications if not properly managed. Understanding hydramnios is crucial for obstetric nursing practice as early detection and intervention can dramatically improve outcomes.
Pathophysiological Mechanisms
Increased Production
- • Maternal diabetes mellitus
- • Fetal urinary tract abnormalities
- • Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome
- • Maternal-fetal blood group incompatibility
Decreased Absorption
- • Fetal gastrointestinal anomalies
- • Esophageal atresia
- • Duodenal atresia
- • Central nervous system disorders
Causes & Risk Factors
| Category | Specific Causes | Incidence (%) | Nursing Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal Factors |
• Diabetes mellitus • Rh incompatibility • Multiple pregnancies • Maternal infections |
25-30% | Monitor glucose levels, assess for signs of infection |
| Fetal Factors |
• CNS anomalies • GI tract defects • Chromosomal abnormalities • Cardiac anomalies |
20-25% | Prepare for detailed fetal assessments and genetic counseling |
| Placental Factors |
• Placental tumors • Chorioangiomas • Twin-to-twin transfusion |
5-10% | Monitor fetal growth patterns and placental function |
| Idiopathic | No identifiable cause | 35-40% | Focus on symptom management and monitoring |
Memory Aid – “MOTHERS”
M – Multiple pregnancies
O – Obstruction (GI/GU)
T – Twin-to-twin transfusion
H – Hydrops fetalis
E – Esophageal atresia
R – Rh incompatibility
S – Skeletal abnormalities
Clinical Manifestations
Maternal Signs & Symptoms
Physical Discomfort
- • Abdominal distension and discomfort
- • Difficulty breathing (dyspnea)
- • Increased fundal height for gestational age
- • Back pain and pressure
- • Difficulty sleeping and positioning
Cardiovascular Effects
- • Lower extremity edema
- • Increased heart rate
- • Varicose veins
- • Supine hypotensive syndrome
Fetal Manifestations
Growth & Position
- • Fetal malpresentation
- • Excessive fetal movement
- • Difficulty palpating fetal parts
- • Unstable fetal lie
Assessment Findings
- • Muffled fetal heart sounds
- • Ballottement easily elicited
- • Fluid thrill on percussion
- • Large-for-gestational-age appearance
Assessment & Diagnosis
Diagnostic Criteria for Hydramnios
| Measurement Method | Normal Range | Mild Hydramnios | Moderate | Severe |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI) | 5-24 cm | 25-29.9 cm | 30-34.9 cm | ≥35 cm |
| Single Deepest Pocket (SDP) | 2-8 cm | 8-11.9 cm | 12-15.9 cm | ≥16 cm |
| Total Volume | 500-1500 mL | 1500-2000 mL | 2000-3000 mL | ≥3000 mL |
Comprehensive Assessment Protocol
History Taking
- • Previous pregnancy history
- • Diabetes screening results
- • Family history of anomalies
- • Current symptoms onset
- • Medication history
Physical Examination
- • Fundal height measurement
- • Leopold’s maneuvers
- • Fetal heart rate assessment
- • Maternal vital signs
- • Edema evaluation
Laboratory Tests
- • Glucose tolerance test
- • Complete blood count
- • Viral titers (TORCH)
- • Rh factor and antibodies
- • Liver function tests
Ultrasound Assessment in Hydramnios
Primary Assessments:
- • Amniotic fluid volume quantification
- • Fetal anatomical survey
- • Placental examination
- • Biophysical profile
Specialized Studies:
- • Doppler flow studies
- • 3D/4D imaging if indicated
- • Fetal echocardiography
- • Serial growth assessments
Nursing Interventions & Care Planning
Priority Nursing Diagnoses
High Priority
- • Risk for impaired gas exchange
- • Risk for injury (maternal/fetal)
- • Acute pain related to abdominal distension
- • Anxiety related to pregnancy complications
Secondary Priority
- • Impaired physical mobility
- • Risk for infection
- • Deficient knowledge regarding condition
- • Risk for ineffective coping
Comprehensive Nursing Care Plan
Respiratory Management
Interventions:
- • Position patient in semi-Fowler’s or left lateral position
- • Monitor respiratory rate and oxygen saturation
- • Teach breathing exercises and relaxation techniques
- • Assess for signs of respiratory distress
Expected Outcomes:
- • Respiratory rate 16-24/min
- • Oxygen saturation >95%
- • Absence of dyspnea at rest
- • Patient reports improved breathing
Maternal Safety & Comfort
Safety Measures:
- • Implement fall prevention protocols
- • Assist with ambulation and position changes
- • Monitor for signs of preterm labor
- • Assess for membrane rupture or leaking
Comfort Interventions:
- • Provide supportive positioning with pillows
- • Apply warm or cool compresses as tolerated
- • Encourage frequent position changes
- • Administer prescribed analgesics
Fetal Monitoring & Assessment
Monitoring Parameters:
- • Continuous or intermittent FHR monitoring
- • Daily fetal movement counts
- • Serial fundal height measurements
- • Biophysical profile assessments
Documentation Requirements:
- • FHR patterns and variability
- • Maternal perception of fetal movement
- • Changes in abdominal circumference
- • Response to interventions
Nursing Intervention Mnemonic – “COMFORT”
C – Continuous monitoring
O – Optimal positioning
M – Mobility assistance
F – Frequent assessments
O – Oxygen support if needed
R – Respiratory support
T – Teaching and education
Medical Management & Treatment Options
Treatment Approaches Based on Severity
| Severity Level | Management Approach | Monitoring Frequency | Nursing Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild (AFI 25-29.9) |
• Conservative management • Activity modification • Regular monitoring • Patient education |
Every 2-4 weeks |
• Symptom assessment • Patient teaching • Support and reassurance |
| Moderate (AFI 30-34.9) |
• Increased surveillance • Corticosteroids if preterm • Consider amniocentesis • Maternal rest |
Every 1-2 weeks |
• Intensive monitoring • Preterm labor surveillance • Medication administration |
| Severe (AFI ≥35) |
• Hospitalization • Therapeutic amniocentesis • Delivery planning • Multidisciplinary care |
Daily to twice daily |
• Continuous assessment • Procedure assistance • Emergency preparedness |
Therapeutic Interventions in Hydramnios
Therapeutic Amniocentesis
Indications:
- • Severe maternal respiratory distress
- • Severe abdominal discomfort
- • Risk of preterm labor
- • Preparation for delivery
Nursing Considerations:
- • Pre-procedure patient preparation
- • Continuous fetal monitoring
- • Post-procedure observation
- • Complication surveillance
Pharmacological Management
Medications Used:
- • Indomethacin (to reduce fetal urine production)
- • Corticosteroids (for fetal lung maturity)
- • Tocolytics (to prevent preterm labor)
- • Analgesics for comfort
Nursing Monitoring:
- • Drug efficacy assessment
- • Side effect monitoring
- • Medication teaching
- • Compliance evaluation
Emergency Management Protocols
Immediate Actions:
- • Assess maternal respiratory status
- • Position for optimal breathing
- • Establish IV access
- • Continuous fetal monitoring
Notifications:
- • Notify obstetrician immediately
- • Alert anesthesia team
- • Prepare OR if needed
- • Contact neonatology
Documentation:
- • Time of symptom onset
- • Interventions performed
- • Patient response
- • Communication log
Complications & Risk Management
Maternal Complications of Hydramnios
Immediate Complications
- • Respiratory distress and dyspnea
- • Preterm labor and delivery
- • Premature rupture of membranes
- • Placental abruption
- • Cord prolapse
- • Maternal discomfort and pain
Labor & Delivery Complications
- • Malpresentation and malposition
- • Prolonged labor
- • Uterine dysfunction
- • Postpartum hemorrhage
- • Operative delivery requirements
- • Anesthesia complications
Fetal & Neonatal Complications
| Complication Category | Specific Risks | Incidence Rate | Prevention Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Congenital Anomalies |
• Neural tube defects • GI tract abnormalities • Chromosomal disorders • Cardiac defects |
15-20% |
• Early detailed ultrasound • Genetic counseling • Amniocentesis for karyotyping |
| Birth Complications |
• Preterm birth • Birth asphyxia • Cord accidents • Delivery trauma |
25-30% |
• Controlled delivery environment • Skilled attendance • NICU readiness |
| Respiratory Issues |
• Respiratory distress syndrome • Pulmonary hypoplasia • Meconium aspiration • Pneumonia |
10-15% |
• Corticosteroid administration • Surfactant therapy • Respiratory support planning |
Complication Alert Mnemonic – “DANGER”
D – Dyspnea and respiratory distress
A – Abruption of placenta
N – Neurological fetal defects
G – Growth abnormalities
E – Early labor onset
R – Rupture of membranes
Prevention Strategies & Health Promotion
Preconception & Early Pregnancy Prevention
Diabetes Management
- • Pre-pregnancy glucose control
- • Regular HbA1c monitoring
- • Nutritional counseling
- • Exercise recommendations
- • Medication optimization
Genetic Counseling
- • Family history assessment
- • Risk factor identification
- • Carrier screening options
- • Prenatal testing discussion
- • Informed decision making
Regular Prenatal Care
- • Early pregnancy registration
- • Scheduled appointments
- • Risk assessment at each visit
- • Timely intervention
- • Patient education
Patient Education Program for Hydramnios Prevention
Comprehensive Education Topics
Lifestyle Modifications:
- • Optimal nutrition during pregnancy
- • Weight management guidelines
- • Safe exercise practices
- • Stress reduction techniques
- • Smoking cessation support
- • Alcohol avoidance education
Warning Signs Education:
- • Excessive abdominal growth
- • Difficulty breathing patterns
- • Decreased fetal movement
- • Signs of preterm labor
- • When to contact healthcare provider
- • Emergency situations recognition
Prevention Mnemonic – “PREVENT”
P – Preconception counseling
R – Regular prenatal visits
E – Early detection screening
V – Vaccination updates
E – Education and awareness
N – Nutritional optimization
T – Timely intervention
Global Best Practices & Innovations
International Excellence in Hydramnios Management
United States – Mayo Clinic Protocol
Innovation Highlights:
- • Multidisciplinary team approach
- • Advanced MRI fetal imaging
- • Personalized treatment algorithms
- • Real-time genetic counseling
Nursing Integration:
- • Specialized nurse coordinators
- • Patient navigation programs
- • Telehealth monitoring systems
- • Family-centered care models
United Kingdom – NICE Guidelines Implementation
Best Practice Elements:
- • Evidence-based care pathways
- • Standardized assessment tools
- • Quality improvement cycles
- • Patient outcome tracking
Nursing Excellence:
- • Competency-based training
- • Peer review processes
- • Continuous professional development
- • Research integration
Sweden – Preventive Care Model
Prevention Focus:
- • Population-based screening
- • Early intervention programs
- • Health promotion initiatives
- • Community partnerships
Midwifery Integration:
- • Continuity of care models
- • Home-based monitoring
- • Psychosocial support systems
- • Cultural competency training
Japan – Technology Integration
Technological Advances:
- • AI-assisted diagnosis systems
- • Wearable monitoring devices
- • Mobile health applications
- • Predictive analytics models
Nursing Technology Use:
- • Digital documentation systems
- • Remote patient monitoring
- • Virtual reality training
- • Electronic decision support
Emerging Innovations in Hydramnios Care
Diagnostic Innovations:
- • 3D/4D ultrasound advances
- • Biomarker development
- • Genetic screening improvements
- • Point-of-care testing
Treatment Advances:
- • Minimally invasive procedures
- • Novel pharmacological agents
- • Fetal therapy options
- • Precision medicine approaches
Care Delivery Models:
- • Integrated care pathways
- • Shared decision-making tools
- • Patient-reported outcomes
- • Quality improvement initiatives
References & Further Reading
Evidence-Based Resources
1. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2024). Practice Bulletin: Polyhydramnios. Obstetrics & Gynecology, 143(2), e45-e52.
2. Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. (2024). Green-top Guideline: Management of Polyhydramnios. RCOG Press.
3. Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. (2024). Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Polyhydramnios. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology, 230(1), B2-B15.
4. International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics. (2024). Global Guidelines: Polyhydramnios Management in Resource-Limited Settings.
5. World Health Organization. (2024). Technical Report: Complications in Pregnancy – Polyhydramnios. WHO Press.
Key Learning Points Summary
Essential Knowledge:
- • Hydramnios affects 1-2% of pregnancies
- • AFI >24cm indicates polyhydramnios
- • 35-40% cases are idiopathic
- • Multidisciplinary approach is essential
Nursing Priorities:
- • Respiratory status monitoring
- • Fetal surveillance protocols
- • Patient education and support
- • Complication prevention strategies
