Care of Patients with Condom Drainage
Comprehensive Nursing Notes & Clinical Implementation Guide
Evidence-Based Practice
Learning Objectives
Upon completion, nursing students will be able to:
- Demonstrate proper application technique for condom catheters
- Identify appropriate candidates for condom catheter use
- Recognize and prevent complications associated with external drainage
- Implement evidence-based monitoring and care protocols
Clinical Competencies:
- Perform comprehensive skin assessment protocols
- Execute proper sizing and measurement techniques
- Provide comprehensive patient and family education
- Document outcomes using standardized nursing languages
Introduction & Anatomical Considerations
Definition & Purpose
A condom catheter, also known as a male external catheter (MEC), Texas catheter, or urinary sheath, is a non-invasive urinary drainage device designed for male patients experiencing urinary incontinence. This external collection system provides an alternative to indwelling urethral catheters, reducing infection risk while maintaining patient dignity and comfort.
The device consists of a flexible, latex or silicone sheath that fits over the penis, connected to a drainage tube and collection bag. Unlike internal catheters, condom catheters do not penetrate the urethral opening, significantly reducing the risk of catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs).
Anatomical Considerations
- Penile anatomy: Understanding glans, corona, shaft, and frenulum is crucial for proper application
- Skin integrity: Penile skin is sensitive and prone to breakdown with improper application
- Circulation: Proper sizing prevents compromised blood flow and tissue necrosis
- Hygiene considerations: Uncircumcised patients require special attention to prevent smegma accumulation
Condom Catheter System Components
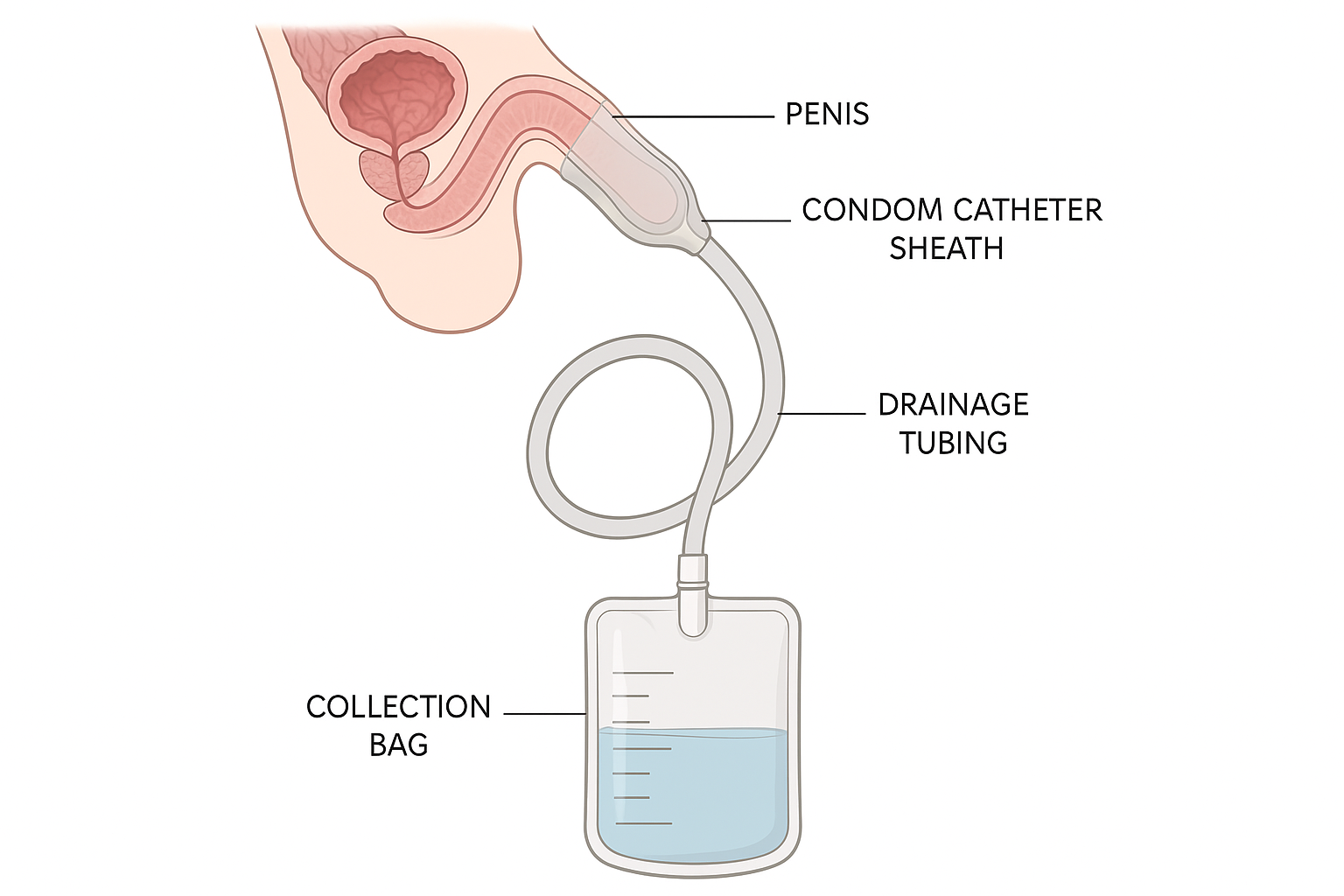
Professional medical illustration demonstrating the proper anatomical placement of a condom catheter system, including the external sheath, drainage tubing, and collection bag components used in male urinary management.
Clinical Indications
Primary Indications:
- Urinary incontinence in cooperative male patients
- Neurogenic bladder with reflex incontinence
- Spinal cord injuries with bladder dysfunction
- Dementia patients with incontinence issues
- Post-operative patients requiring urinary management
Secondary Indications:
- Accurate urine output monitoring in incontinent patients
- Skin protection from chronic moisture exposure
- Temporary use during acute illness episodes
- Alternative to indwelling catheter when appropriate
Contraindications & Precautions
Absolute Contraindications:
- Urinary retention or bladder outlet obstruction
- Severe cognitive impairment with agitation
- Existing penile lesions or open wounds
- Severe penile retraction or micropenis
- Latex allergy (unless silicone alternative available)
Relative Contraindications:
- Frequent manipulation or pulling at catheter
- Severe peripheral edema affecting genital area
- History of recurrent catheter-related complications
- Inadequate caregiver support for proper maintenance
Equipment & Supplies
Essential Equipment:
- Condom catheter (appropriate size and type)
- Skin prep solution or barrier film
- Drainage tubing and collection bag
- Adhesive strips or securing device
- Mild soap and warm water
- Clean towels and washcloths
Additional Supplies:
- Disposable gloves (non-latex if allergy present)
- Measuring tape for proper sizing
- Scissors for trimming hair if necessary
- Catheter removal solution or adhesive remover
- Leg bag or bedside drainage bag
- Documentation materials
Proper Sizing & Measurement Technique
Measurement Protocol:
- 1 Measure penile circumference at the base using a flexible measuring tape
- 2 Divide circumference by 3.14 (π) to determine diameter
- 3 Select catheter size based on calculated diameter
- 4 Ensure proper fit – not too tight or loose
Size Selection Guide:
| Size | Diameter (mm) | Circumference (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Small | 25-30 | 78-94 |
| Medium | 31-35 | 97-110 |
| Large | 36-40 | 113-126 |
| Extra Large | 41-45 | 129-141 |
Memory Aid: “SECURE” Application Protocol
Mnemonic: S-E-C-U-R-E
- S Size – Measure and select appropriate catheter size
- E Examine – Assess skin integrity and anatomical suitability
- C Clean – Thoroughly cleanse and dry the area
- U Unroll – Apply catheter smoothly with proper spacing
- R Reconnect – Attach drainage tubing securely
- E Evaluate – Check for proper fit and function
Application Tips:
Clinical Pearl:
Always leave 1-2 inches of space between the glans penis and the catheter tip to prevent trauma and ensure proper drainage. This “safety zone” prevents pressure necrosis and allows for normal penile movement.
Nursing Tip:
Document the exact size used and any patient-specific considerations for future reference. This ensures consistency in care and helps identify patterns or issues over time.
Step-by-Step Application Procedure
Pre-Application Phase:
Gather Equipment
Collect all necessary supplies and ensure proper catheter size is available. Verify expiration dates and package integrity.
Patient Preparation
Explain procedure to patient, ensure privacy, and position patient comfortably. Obtain informed consent if required.
Hand Hygiene
Perform thorough hand hygiene and don non-sterile gloves. Consider using non-latex gloves if allergy concerns exist.
Skin Assessment
Examine penile skin for lesions, rashes, or areas of breakdown. Document any abnormal findings.
Application Phase:
Cleansing
Gently cleanse penis with mild soap and warm water. Pay special attention to uncircumcised patients. Pat dry thoroughly.
Hair Removal
Trim excess hair around the base of penis if necessary. Use scissors rather than razors to prevent nicks.
Skin Preparation
Apply skin prep solution or barrier film if indicated. Allow to dry completely before proceeding.
Catheter Application
Hold penis firmly but gently. Roll catheter onto penis from tip toward base, leaving appropriate space at the tip.
Securing & Connection:
Secure Attachment
Ensure catheter is securely attached but not too tight. Check for proper seal around the base.
Connect Drainage
Attach drainage tubing to catheter. Ensure connection is secure and leak-free.
Position Drainage Bag
Position collection bag below bladder level. Secure tubing to prevent kinking or disconnection.
Post-Application:
Function Check
Verify proper urine flow and absence of leakage. Check for comfort and appropriate fit.
Patient Education
Educate patient and family about catheter care, signs of complications, and when to seek help.
Documentation
Document procedure, catheter size, patient tolerance, and any concerns noted during application.
Ongoing Nursing Care & Monitoring
Daily Assessment Protocol:
Skin Integrity Assessment
- • Inspect for redness, irritation, or breakdown
- • Check for signs of allergic reaction
- • Assess for pressure points or constriction
- • Document any changes in skin condition
Catheter Function Check
- • Verify proper urine flow and drainage
- • Check for leakage around catheter
- • Ensure drainage bag is positioned correctly
- • Assess for kinking or obstruction in tubing
Monitoring Schedule:
Every 8 Hours:
- • Empty and measure drainage bag
- • Check catheter position and security
- • Assess patient comfort level
- • Document urine output and characteristics
Every 24 Hours:
- • Complete skin assessment
- • Review catheter need and appropriateness
- • Assess for signs of infection
- • Evaluate overall patient response
Complications & Prevention Strategies
Common Complications:
Skin Breakdown
Signs: Redness, irritation, blistering, or ulceration
Risk Factors: Prolonged use, improper sizing, poor hygiene
Prevention: Regular skin assessment, proper sizing, daily catheter changes
Urinary Tract Infection
Signs: Fever, burning sensation, cloudy urine, foul odor
Risk Factors: Poor hygiene, contaminated equipment, prolonged use
Prevention: Strict aseptic technique, proper hygiene, regular catheter changes
Catheter Displacement
Signs: Leakage, catheter slipping, inability to collect urine
Risk Factors: Incorrect size, patient movement, inadequate securing
Prevention: Proper sizing, secure application, patient education
Serious Complications:
Penile Necrosis
Signs: Discoloration, tissue death, severe pain
Emergency Action: Immediate catheter removal, urgent medical consultation
Prevention: Proper sizing, avoid over-tightening, regular monitoring
Circulatory Compromise
Signs: Swelling, color changes, numbness, decreased sensation
Emergency Action: Immediate assessment, possible catheter removal
Prevention: Frequent circulation checks, proper application technique
Severe Allergic Reaction
Signs: Widespread rash, difficulty breathing, systemic symptoms
Emergency Action: Immediate catheter removal, emergency treatment
Prevention: Allergy screening, alternative materials, patch testing
Evidence-Based Prevention Strategies
Skin Protection:
- Use barrier films or skin protectants
- Rotate catheter position when possible
- Maintain proper skin hygiene
- Monitor for early signs of breakdown
Infection Prevention:
- Maintain strict aseptic technique
- Use clean technique for routine care
- Change catheter as per protocol
- Monitor for signs of infection
System Integrity:
- Ensure proper catheter sizing
- Secure all connections properly
- Maintain closed drainage system
- Regular system inspection
Patient & Family Education
Self-Care Instructions:
Daily Hygiene:
- • Wash hands before and after touching catheter
- • Clean genital area with mild soap and water daily
- • Pat skin dry thoroughly after cleaning
- • Avoid harsh soaps or perfumed products
Catheter Management:
- • Empty drainage bag regularly (every 8 hours)
- • Keep drainage bag below bladder level
- • Avoid kinking or twisting of tubing
- • Change catheter as instructed by healthcare provider
When to Seek Help:
Immediate Medical Attention:
- • Severe pain or discomfort
- • Signs of infection (fever, chills, foul odor)
- • Skin breakdown or open wounds
- • Catheter falls off repeatedly
- • Blood in urine
- • Difficulty urinating or no urine output
Routine Follow-up:
- • Regular skin assessment and care
- • Catheter sizing and fit evaluation
- • Review of application technique
- • Assessment of continued need
Quality Indicators & Documentation
Key Performance Metrics:
Safety Indicators:
- • Zero incidents of pressure necrosis
- • Skin integrity maintained in 95% of patients
- • Catheter-related UTI rate <2%
- • Successful catheter retention >90%
Patient Satisfaction:
- • Comfort level rating >7/10
- • Dignity and privacy maintained
- • Educational needs met
- • Family satisfaction with care
Documentation Requirements:
Initial Application:
- • Date and time of application
- • Catheter size and type used
- • Skin condition at baseline
- • Patient tolerance and response
- • Education provided
Ongoing Care:
- • Daily skin assessment findings
- • Urine output and characteristics
- • Catheter function and integrity
- • Patient comfort and satisfaction
- • Complications or concerns
Evidence-Based Practice & Research
Current Research Findings:
Infection Prevention:
Recent studies demonstrate that condom catheters have a significantly lower infection rate compared to indwelling catheters (2.5% vs 15.2%).
Source: Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing, 2023
Skin Integrity:
Daily catheter changes reduce skin complications by 40% compared to prolonged use schedules.
Source: International Journal of Nursing Studies, 2022
Best Practice Guidelines:
CDC Recommendations:
- • Use only when clinically indicated
- • Implement daily catheter necessity review
- • Maintain closed drainage system
- • Follow manufacturer’s instructions
Professional Standards:
- • ANA Standards of Practice compliance
- • Joint Commission safety goals
- • Evidence-based care protocols
- • Continuous quality improvement
Clinical Decision-Making Flowchart
• Male patient
• Cooperative
• No contraindications
• Measure and size
• Apply using SECURE protocol
• Monitor regularly
• Contraindications present
• Unable to cooperate
• Anatomical limitations
• Scheduled toileting
• Incontinence products
• Other catheter types
Key Takeaways & Summary
Essential Nursing Competencies:
- Master the SECURE application protocol for consistent, safe catheter placement
- Implement evidence-based monitoring and assessment protocols
- Recognize and prevent complications through proactive care
- Provide comprehensive patient and family education
Critical Safety Points:
- Proper sizing is crucial – too tight causes necrosis, too loose causes leakage
- Daily skin assessment prevents serious complications
- Maintain closed drainage system to prevent infection
- Regular catheter changes reduce complication risk
Additional Memory Aid: “CARE” Documentation
C-A-R-E Documentation Framework:
- C Condition – Document skin condition and catheter function
- A Assessment – Record patient comfort and tolerance
- R Response – Note patient/family response to education
- E Evaluation – Assess effectiveness and plan next steps
Quality Checklist:
Before Every Shift:
- ☐ Skin assessment completed
- ☐ Catheter function verified
- ☐ Drainage bag emptied and measured
- ☐ Patient comfort assessed
- ☐ Documentation updated
- ☐ Education reinforced as needed
References & Further Reading
Professional Guidelines:
- • Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024). Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention.
- • European Association of Urology Nurses. (2023). Male External Catheters in Adults: Clinical Practice Guidelines.
- • American Nurses Association. (2023). Standards of Practice for Continence Care.
- • Joint Commission. (2024). National Patient Safety Goals: Infection Prevention.
Research Articles:
- • Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing (2023). “Comparative Study of External vs. Internal Catheters.”
- • International Journal of Nursing Studies (2022). “Daily Catheter Changes and Skin Integrity.”
- • Rehabilitation Nursing Journal (2023). “Male External Catheter Care and Maintenance.”
- • Urology Today (2024). “Complications and Adverse Events in External Catheter Use.”
