Healthcare Information Systems
Architecture and Role in Modern Healthcare Environments
Table of Contents
Introduction to Healthcare Information Systems
Healthcare Information Systems (HIS) are comprehensive, integrated information systems designed to manage the administrative, financial, and clinical aspects of a healthcare facility. These systems serve as the technological backbone of modern healthcare delivery, enabling efficient data management, improved clinical decision-making, and enhanced patient care.
Key Definition
A Healthcare Information System is a socio-technical system that comprises all information processing components, including the associated human or technical actors, that contribute to the functional organization of a healthcare facility.
The evolution of healthcare information systems has transformed from simple administrative tools to sophisticated platforms that support clinical workflows, patient care, research, and healthcare management. This evolution reflects the growing recognition of the importance of efficient information processing in delivering quality healthcare services.
For nursing professionals, understanding these systems is crucial as they form an integral part of daily clinical practice, documentation, and patient care planning. Nurses interact with various components of healthcare information systems throughout their shifts, making it essential to comprehend their architecture, function, and optimal use.
Importance and Benefits of Healthcare Information Systems
The implementation of well-designed healthcare information systems offers numerous benefits to healthcare organizations, providers, and patients. Understanding these benefits highlights the critical role these systems play in modern healthcare environments.
Improved Patient Safety
Automated alerts for drug interactions, allergies, and dosage errors significantly reduce medication errors and adverse events.
Enhanced Clinical Decision-Making
Access to comprehensive patient data, evidence-based guidelines, and decision support tools helps clinicians make informed decisions.
Streamlined Workflow
Automated processes reduce administrative burden, allowing healthcare providers to focus more on patient care activities.
Improved Data Integration
Centralized systems enable seamless sharing of patient information across departments, reducing duplication and improving continuity of care.
Enhanced Communication
Digital communication channels facilitate better coordination among healthcare team members, improving collaborative care.
Improved Resource Utilization
Data analytics capabilities help optimize resource allocation, reduce waste, and improve operational efficiency.
For nursing professionals, these systems support evidence-based practice, reduce documentation time, and facilitate better care coordination. The integration of nursing workflows into healthcare information systems has become crucial for delivering high-quality patient care in today’s healthcare environment.
Healthcare Information System Architecture
The architecture of healthcare information systems provides a structured framework for understanding how different components interact and support healthcare delivery. A well-designed architecture ensures that the system can effectively meet clinical and administrative needs while maintaining security, scalability, and interoperability.
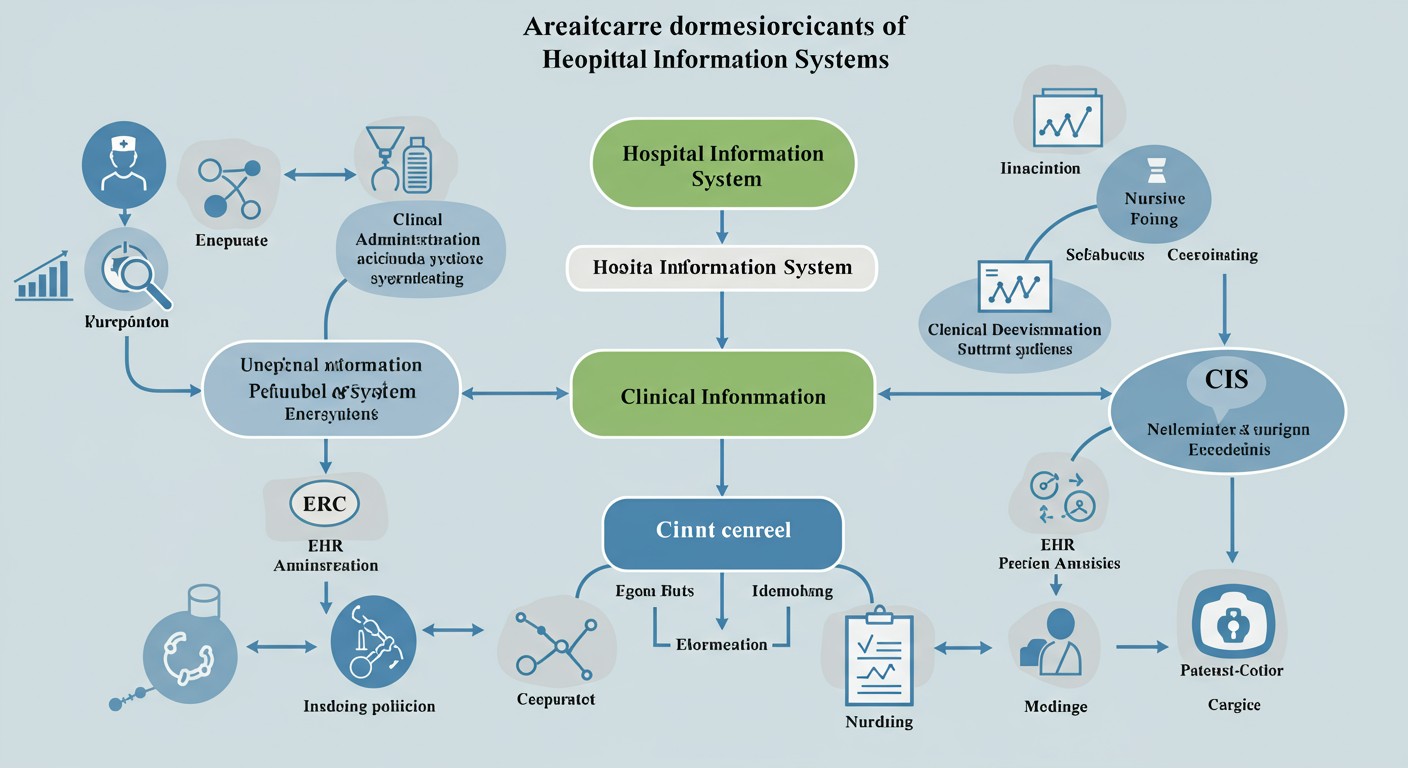
Figure 1: Comprehensive Healthcare Information System Architecture
Architectural Views
Healthcare information system architecture can be described using four main architectural views:
| Architectural View | Description | Relevance to Nursing |
|---|---|---|
| Context Diagram | Illustrates how the system interacts with external entities (patients, providers, other systems) | Helps nurses understand how patient data flows between systems and stakeholders |
| Decomposition View | Breaks down the system into functional modules and components | Shows which modules nurses will interact with (documentation, medication, orders) |
| Layered View | Organizes system components into logical layers (presentation, business logic, data) | Explains how the user interface connects to underlying data and processes |
| Deployment View | Shows how system components are distributed across physical infrastructure | Helps understand why some systems may be accessible from certain workstations |
Three-Layer Model of Health Information Systems
Health information systems can be conceptualized using a three-layer model:
Domain Layer
Describes entity types (patients, providers, facilities) and healthcare functions (clinical care, administration)
Logical Tool Layer
Describes applications, components, and services that support domain layer functions
Physical Implementation Layer
Describes hardware, networks, and physical data storage solutions
Understanding this architectural framework helps nursing professionals contextualize their role within the broader healthcare information ecosystem and how data flows through various systems to support patient care.
Hospital Information Systems (HIS)
Hospital Information Systems (HIS) are comprehensive, integrated information systems designed to manage administrative, financial, and clinical aspects of a hospital’s operations. They serve as the technological backbone of hospital management, coordinating various functions to ensure smooth operations and effective patient care.
Key Definition
A Hospital Information System (HIS) is a comprehensive, integrated information system designed to manage all aspects of a hospital’s operation, including administrative, financial, and clinical activities. It enables the hospital to enhance efficiency through improved patient care, cost control, and reduced paperwork.
Core Components of Hospital Information Systems
Administrative Components
- Patient Registration and Management
- Appointment Scheduling
- Bed Management
- Admission, Discharge, Transfer (ADT) System
- Staff Management
Financial Components
- Billing and Invoicing
- Insurance Claims Processing
- Financial Accounting
- Inventory Management
- Payroll Management
Clinical Components
- Electronic Health Records (EHR)
- Computerized Provider Order Entry (CPOE)
- Clinical Documentation
- Pharmacy Management
- Laboratory Information System
Support Components
- Reporting and Analytics
- Decision Support Systems
- Communication Systems
- Security and Access Control
- Data Backup and Recovery
Types of Hospital Information Systems
Hospital information systems can be categorized based on their scope and implementation approach:
| Type | Description | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Integrated HIS | A single system that covers all hospital functions | Seamless data integration, consistent user interface | Higher implementation cost, vendor lock-in |
| Best-of-Breed HIS | Combines specialized systems from different vendors | Best functionality in each area, flexibility | Integration challenges, multiple interfaces to learn |
| Cloud-Based HIS | Hosted on remote servers, accessed via internet | Lower upfront costs, easier maintenance | Requires reliable internet connection, potential security concerns |
| On-Premises HIS | Installed and operated on hospital’s own servers | Greater control over data, potential security advantages | Higher IT staffing requirements, higher initial costs |
Nursing professionals interact with multiple components of the HIS during their daily workflow. Understanding the structure and integration of these components helps nurses navigate the system efficiently, ensuring they can access the information they need to provide quality patient care while meeting documentation requirements.
Clinical Information Systems (CIS)
Clinical Information Systems (CIS) are specialized components of healthcare information technology focused specifically on capturing, storing, manipulating, and making available clinical information important to the healthcare delivery process. These systems directly support patient care activities and clinical decision-making.
Key Definition
A Clinical Information System (CIS) is a computer-based system that is designed to collect, store, manipulate, and make available clinical information essential to the healthcare delivery process. It focuses on the clinical aspects of patient care rather than administrative or financial functions.
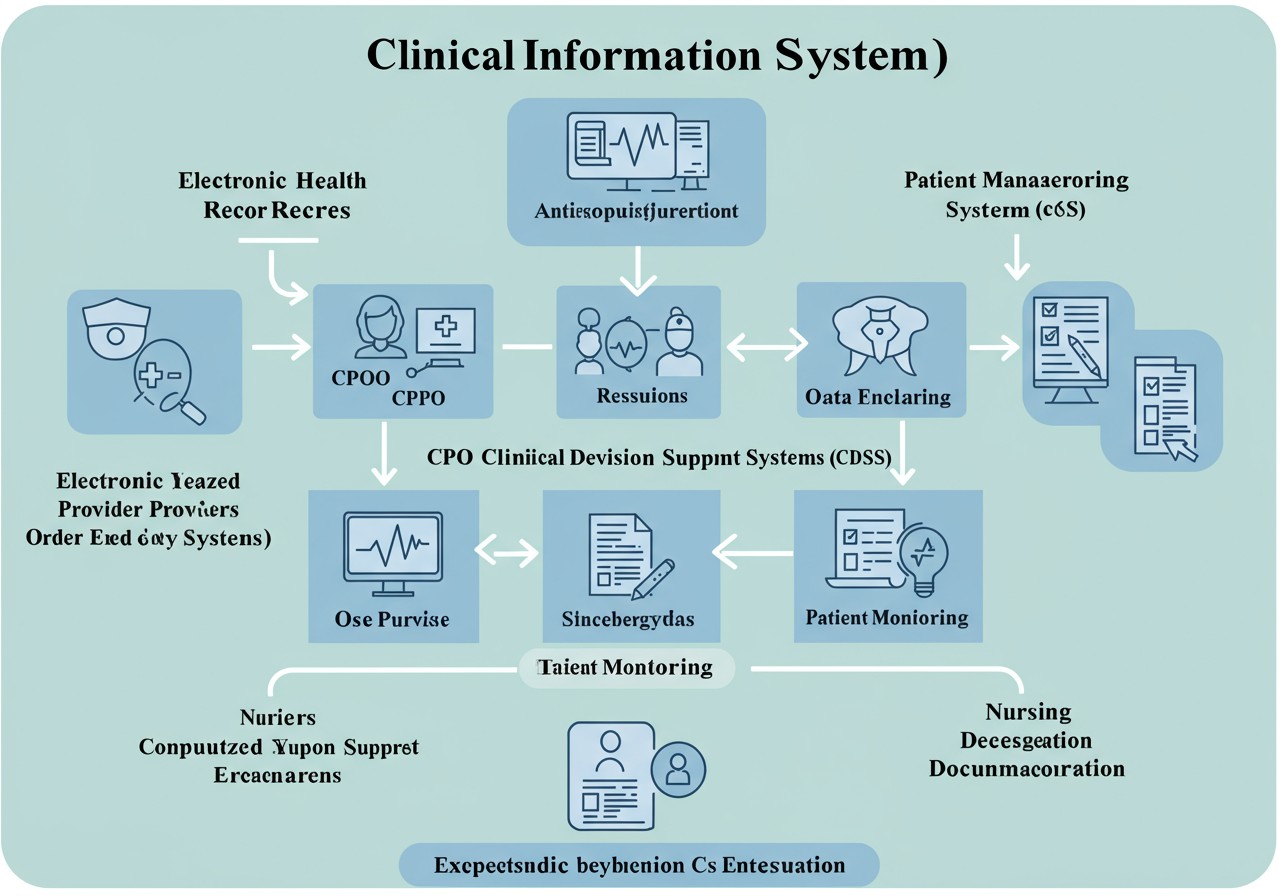
Figure 2: Clinical Information System Components and Nursing Interaction
Core Components of Clinical Information Systems
| Component | Function | Nursing Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Electronic Health Records (EHR) | Digital version of patient’s medical history, including demographics, progress notes, medications, vital signs, past medical history, etc. | Primary tool for documenting assessments, interventions, and patient responses |
| Computerized Provider Order Entry (CPOE) | System for healthcare providers to enter medical orders electronically | Allows nurses to receive, verify, and implement orders efficiently |
| Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) | Provides clinicians with knowledge and person-specific information to enhance clinical decisions | Supports nurses with alerts, reminders, and evidence-based care recommendations |
| Results Management | Stores and organizes laboratory, radiology, and other diagnostic test results | Enables nurses to access test results promptly to inform patient care |
| Medication Administration Systems | Facilitates safe medication ordering, dispensing, and administration | Supports the five rights of medication administration and documentation |
| Patient Monitoring Systems | Collects and displays physiological data from monitoring devices | Allows continuous assessment of patient condition and early detection of changes |
| Nursing Documentation Systems | Specialized tools for documenting nursing assessments, care plans, and interventions | Streamlines nursing workflow and ensures comprehensive documentation |
CIS Integration in Nursing Workflow
Clinical Information Systems are deeply integrated into nursing workflows, supporting various aspects of the nursing process:
Assessment
Supports structured documentation of patient assessments, vital signs, and observations
Diagnosis
Provides access to clinical decision support tools for identifying nursing diagnoses
Planning
Facilitates development of individualized care plans with evidence-based interventions
Implementation
Supports documentation of nursing interventions, medication administration, and care delivery
Evaluation
Enables tracking of patient outcomes and effectiveness of nursing interventions
Communication
Facilitates interdisciplinary communication and care coordination
The effective use of Clinical Information Systems by nurses can significantly enhance patient care quality, safety, and efficiency. Understanding the structure and functionality of these systems is essential for modern nursing practice.
Data Integration in Healthcare
Data integration in healthcare refers to the process of combining data from multiple disparate sources into a unified view. This integration is crucial for creating a comprehensive picture of patient health, supporting clinical decision-making, and enabling efficient healthcare delivery.
Key Definition
Healthcare data integration is the structured process of gathering, harmonizing, and disseminating varied healthcare data from multiple contributors within the healthcare ecosystem into a unified, consistent format that supports improved patient care, operational efficiency, and clinical decision-making.
Importance of Data Integration
Holistic Patient View
Integration combines clinical, administrative, and financial data to create a comprehensive picture of the patient’s health status and care journey.
Continuity of Care
Ensures that healthcare providers have access to complete patient information regardless of where previous care was received.
Improved Analytics
Integrated data enables more comprehensive analysis for quality improvement, resource allocation, and population health management.
Enhanced Patient Safety
Access to complete medication history, allergies, and previous adverse events helps prevent medical errors and improve safety.
Challenges in Healthcare Data Integration
| Challenge | Description | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Data Heterogeneity | Different systems use different data formats, structures, and terminologies | Implementation of standardized terminologies (SNOMED CT, LOINC, RxNorm); Data mapping and transformation |
| Legacy Systems | Older systems may lack modern integration capabilities | Integration middleware; API development; Staged modernization |
| Privacy and Security | Integration must maintain data privacy and comply with regulations | Role-based access control; Data encryption; Audit trails; Compliance monitoring |
| Data Quality Issues | Inconsistent or inaccurate data can compromise integration efforts | Data validation rules; Data cleaning processes; Data governance frameworks |
| Organizational Barriers | Resistance to sharing data across departments or organizations | Stakeholder engagement; Clear governance policies; Demonstrating value |
Integration Approaches in Healthcare
Health Information Exchange (HIE)
Enables sharing of clinical information across different healthcare organizations within a region, community, or hospital system.
Example: Regional HIEs that connect hospitals, clinics, laboratories, and pharmacies to share patient data.
Interoperability Standards
Technical standards that enable different systems to work together, including HL7, FHIR, DICOM, and IHE profiles.
Example: Using HL7 FHIR for standardized API-based integration between systems.
Enterprise Data Warehouse
Centralized repository that integrates data from multiple sources for reporting and analytics.
Example: Clinical data warehouse that combines EHR, billing, and operational data for quality reporting.
API-Based Integration
Application Programming Interfaces that allow different systems to communicate and share data in real-time.
Example: EHR system that uses APIs to integrate with specialty systems like radiology or laboratory.
For nurses, successful data integration means having access to complete patient information at the point of care, enabling more informed clinical decisions and reducing the time spent searching for information across multiple systems. The integration of clinical data also supports nursing documentation by pre-populating information and reducing redundant data entry.
Nursing Informatics and HIS/CIS
Nursing informatics is a specialty that integrates nursing science with multiple information and analytical sciences to identify, define, manage, and communicate data, information, knowledge, and wisdom in nursing practice. It plays a crucial role in the development, implementation, and optimization of healthcare information systems to support nursing care.
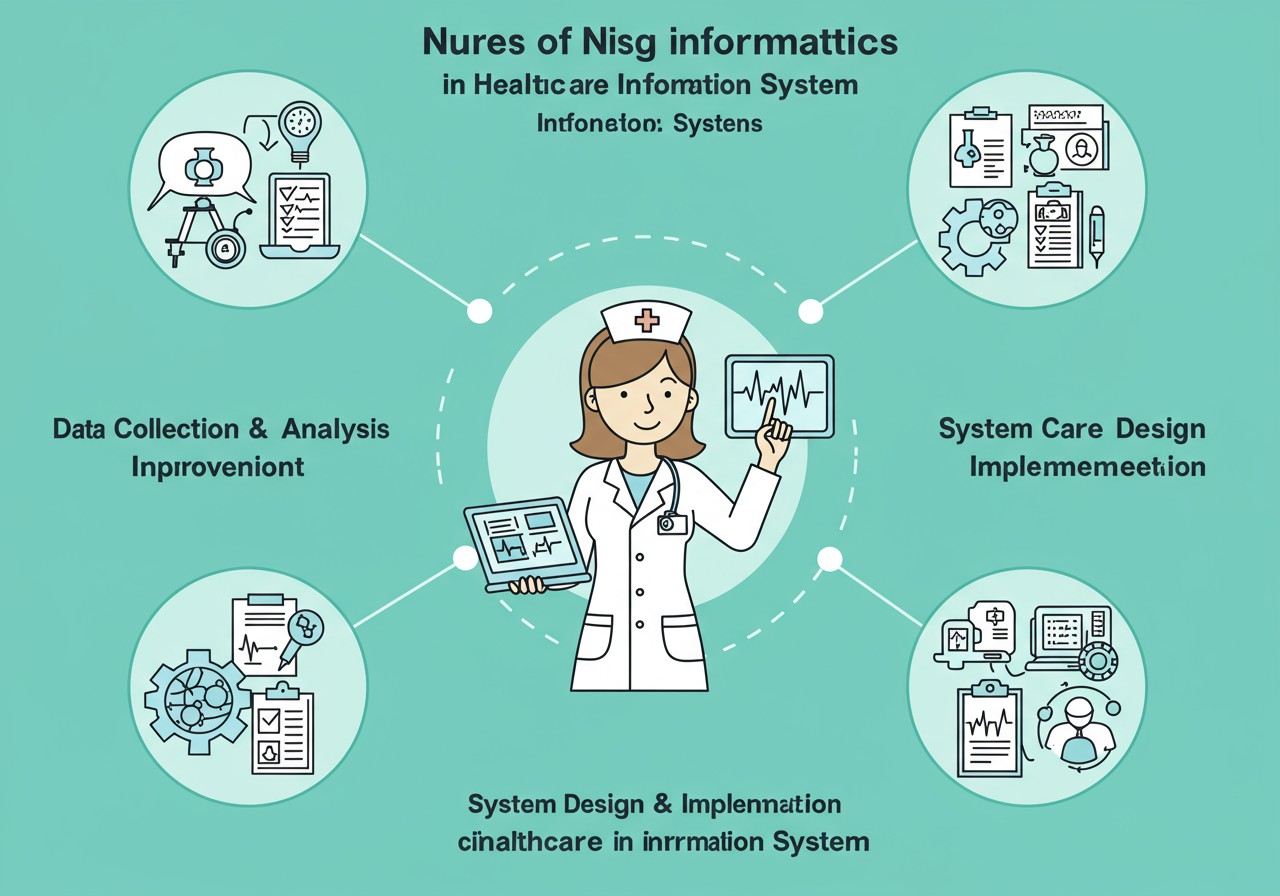
Figure 3: Nursing Informatics Role in Healthcare Information Systems
Key Definition
The American Nurses Association (ANA) defines nursing informatics as “the specialty that integrates nursing science with multiple information and analytical sciences to identify, define, manage and communicate data, information, knowledge, and wisdom in nursing practice.”
Roles of Nursing Informatics in HIS/CIS
System Design and Development
Nurse informaticists collaborate with IT professionals to ensure that healthcare information systems reflect nursing workflows and address clinical needs. They provide critical input on user interface design, data fields, terminology, and clinical decision support features.
Education and Training
They develop and deliver education programs to help nursing staff effectively use healthcare information systems. This includes initial training, ongoing education, and support for new features or updates.
Data Analysis and Quality Improvement
Nurse informaticists leverage data from healthcare information systems to identify patterns, trends, and opportunities for quality improvement. They help translate raw data into actionable insights for nursing practice.
System Implementation
They play a crucial role in the implementation of new systems or updates, serving as a bridge between technical teams and clinical staff. This includes workflow analysis, testing, and change management.
Nursing-Specific Components in HIS/CIS
| Component | Purpose | Benefits for Nursing Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Nursing Documentation Systems | Structured documentation of nursing assessments, interventions, and outcomes | Reduces documentation time, improves completeness, supports continuity of care |
| Care Planning Tools | Development and management of individualized patient care plans | Standardizes care approaches, incorporates evidence-based practices |
| Workload Management Systems | Tracking patient acuity and nursing workload | Supports appropriate staffing, balanced assignments, resource allocation |
| Medication Administration Records | Documentation of medication administration with barcode verification | Reduces medication errors, improves safety, supports compliance |
| Nursing Knowledge Resources | Integration of evidence-based guidelines and references | Provides point-of-care access to best practices and clinical guidance |
Data Integration for Nursing Practice
Effective data integration is particularly important for nursing practice in healthcare information systems:
- Comprehensive Patient View: Integration provides nurses with a complete picture of the patient’s health status, including history, medications, allergies, and recent test results, supporting holistic care.
- Streamlined Documentation: Integration reduces redundant data entry by allowing information to flow between different components of the system.
- Improved Handoffs: Integrated systems facilitate more effective shift handoffs and transitions of care by ensuring all relevant information is accessible.
- Enhanced Decision Support: Integration enables more sophisticated clinical decision support by considering a broader range of patient data.
- Quality Measurement: Integrated data supports the measurement of nursing-sensitive outcomes and quality indicators.
As healthcare continues to digitize, the role of nursing informatics in shaping and optimizing information systems becomes increasingly important. Nurses at all levels benefit from understanding how these systems support their practice and how they can effectively leverage technology to improve patient care.
Challenges and Future Directions
While healthcare information systems offer numerous benefits, they also present challenges that must be addressed to maximize their potential. Understanding these challenges and future trends helps nursing professionals adapt to the evolving healthcare technology landscape.
Current Challenges
Usability Issues
Many healthcare information systems have complex interfaces that can be difficult to navigate, leading to inefficiency and user frustration.
Nursing Impact: Increased documentation time, potential for workarounds that compromise data integrity
Integration Challenges
Difficulties in achieving seamless integration between different systems and modules within the healthcare ecosystem.
Nursing Impact: Need to access multiple systems, incomplete patient information, redundant data entry
Alert Fatigue
Excessive or irrelevant alerts can lead to users ignoring important notifications, compromising patient safety features.
Nursing Impact: Potential to miss critical alerts, increased cognitive burden, workflow interruptions
Training and Adaptation
Healthcare professionals require ongoing training to effectively use evolving systems and features.
Nursing Impact: Learning curve with new systems, need for continuous education, potential resistance to change
Future Directions
| Trend | Description | Potential Impact on Nursing |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning | Integration of AI/ML to analyze patterns, predict outcomes, and support clinical decision-making | Enhanced early warning systems, predictive analytics for patient deterioration, automated documentation assistance |
| Interoperability Advancements | Improved standards and technologies for seamless data exchange between systems | More comprehensive patient information, reduced data entry burden, improved care coordination |
| Patient-Generated Health Data Integration | Incorporation of data from wearables, home monitoring, and patient-reported outcomes | Broader perspective on patient health, remote monitoring capabilities, more personalized care planning |
| Voice Recognition and Natural Language Processing | Advanced voice technology for documentation and system interaction | Reduced typing, hands-free documentation, more efficient workflow |
| Advanced Visualization and Analytics | Sophisticated data visualization tools and analytics for clinical data | Improved trend identification, better understanding of patterns, enhanced quality improvement |
Strategies for Successful Adaptation
Continuous Learning
Engage in ongoing education about healthcare information systems and their applications in nursing practice
Active Participation
Volunteer for implementation teams or user groups to provide nursing perspective in system design and optimization
Critical Evaluation
Assess system functionality in relation to nursing workflow and patient care needs; provide constructive feedback
As healthcare information systems continue to evolve, nurses play a vital role in shaping their development and implementation. By understanding current challenges and future trends, nursing professionals can advocate for systems that truly enhance patient care while supporting efficient clinical workflows.
Mnemonics and Learning Tools
Mnemonics and learning tools can help nursing students remember key concepts related to healthcare information systems. These memory aids are designed to make complex information more accessible and easier to recall during clinical practice.
SYSTEMS: Key Components of HIS
- Scheduling and registration modules
- Yield management for financial operations
- Storage of clinical and administrative data
- Treatment ordering and results management
- Electronic health records for patient information
- Medication management and pharmacy systems
- Security and privacy protection features
CHART: Benefits of Clinical Information Systems
- Continuity of care improvement
- Higher quality patient outcomes
- Automation of routine tasks
- Reduction in medical errors
- Timely access to patient information
DIGITAL: Nursing Considerations for HIS
- Documentation requirements and standards
- Integration with nursing workflow
- Governance and policy compliance
- Information security and privacy
- Technology limitations and workarounds
- Adaptability to changing requirements
- Learning curve and training needs
INTEGRATES: Data Integration Principles
- Interoperability standards adherence
- Normalization of data formats
- Timely synchronization between systems
- Efficient data transfer mechanisms
- Governance frameworks for data management
- Reliable connection between systems
- Authentication and access controls
- Terminology standardization
- Error handling procedures
- Security measures for data protection
Concept Map: Healthcare Information Systems
A concept map helps visualize the relationships between different components of healthcare information systems. Here’s a hierarchical structure to help organize key concepts:
- Healthcare Information Systems
- Hospital Information Systems (HIS)
- Administrative Modules
- Financial Modules
- Clinical Modules
- Clinical Information Systems (CIS)
- Electronic Health Records
- CPOE Systems
- Clinical Decision Support
- Nursing Documentation
- Integration Mechanisms
- Health Information Exchange
- Interoperability Standards
- APIs and Integration Engines
- User Interfaces
- Desktop Applications
- Mobile Applications
- Web Portals
- Hospital Information Systems (HIS)
Quick Reference: Information System Categories
| System Type | Primary Function | Examples | Nursing Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Administrative | Patient registration, scheduling, billing | ADT systems, Practice Management Systems | Patient identification, bed management |
| Clinical Documentation | Recording patient care activities | EHR, Nursing Documentation Systems | Primary user for assessments, interventions, outcomes |
| Order Entry | Entering and managing clinical orders | CPOE, e-Prescribing | Order verification, implementation, documentation |
| Results Reporting | Managing and displaying test results | Laboratory IS, Radiology IS | Results review, patient notification, follow-up |
| Decision Support | Providing clinical guidance and alerts | CDSS, Drug Interaction Checkers | Alert response, clinical decision-making |
Summary
Healthcare Information Systems (HIS) and Clinical Information Systems (CIS) form the technological backbone of modern healthcare delivery, supporting both administrative functions and clinical care processes. These systems have evolved significantly over time, becoming increasingly sophisticated and integrated.
Key Takeaways
- Healthcare information system architecture provides a structured framework for understanding how different components work together to support healthcare delivery.
- Hospital Information Systems (HIS) encompass administrative, financial, and clinical components that manage various aspects of hospital operations.
- Clinical Information Systems (CIS) focus specifically on supporting clinical workflows and patient care activities.
- Data integration in healthcare connects disparate systems and data sources to create a comprehensive view of patient information.
- Nursing informatics plays a crucial role in the design, implementation, and optimization of healthcare information systems.
- While these systems offer numerous benefits, they also present challenges related to usability, integration, and workflow adaptation.
- Future trends include AI/ML integration, improved interoperability, and enhanced patient data integration.
For nursing professionals, understanding healthcare information systems is essential for providing high-quality patient care in today’s technology-enabled healthcare environment. By leveraging these systems effectively, nurses can enhance their practice, improve patient outcomes, and contribute to the ongoing evolution of healthcare technology.
The integration of various healthcare information systems creates a comprehensive ecosystem that supports the entire continuum of care. This integration enables seamless sharing of patient information, streamlines clinical workflows, and facilitates better communication among healthcare team members. When properly implemented and utilized, these systems become powerful tools that enhance both the efficiency and quality of healthcare delivery.
As healthcare continues to evolve, information systems will play an increasingly important role in supporting evidence-based practice, quality improvement, and patient-centered care. Nursing professionals who understand and effectively utilize these systems will be well-positioned to thrive in the digital healthcare landscape of the future.
