Nursing Care Plan for Bladder Irrigation
Comprehensive Guide for Nursing Students
Introduction to Bladder Irrigation
Bladder irrigation is a critical nursing intervention involving the instillation of sterile fluid into the bladder to flush out blood clots, debris, or to administer medications. This procedure is essential in post-surgical care, particularly following urological procedures such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or bladder surgery.
Key Learning Objectives
- Understand the indications for bladder irrigation
- Develop comprehensive nursing care plans
- Identify potential complications and interventions
- Master documentation requirements
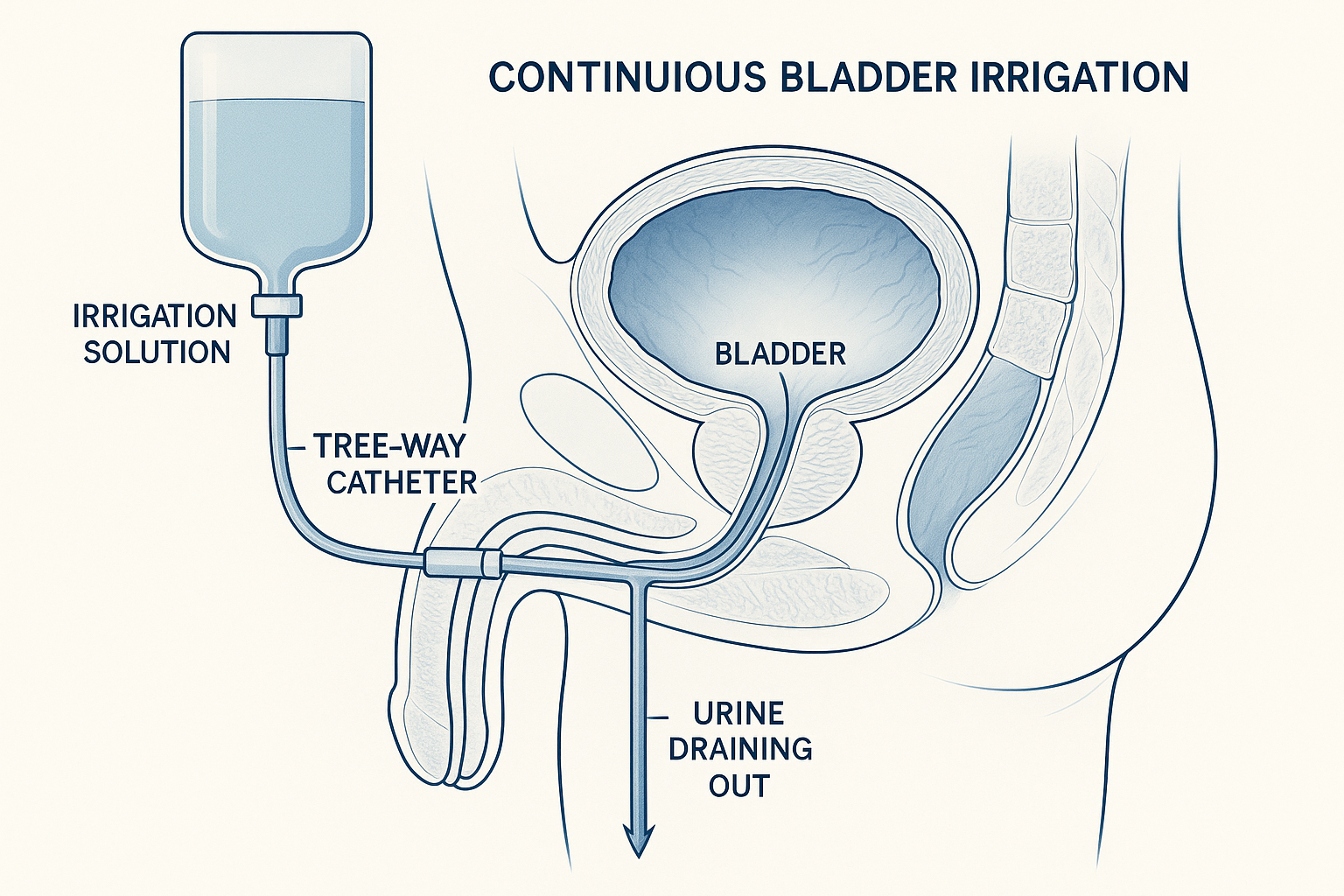
Continuous Bladder Irrigation System – Three-way catheter setup
Types of Bladder Irrigation
Continuous Bladder Irrigation (CBI)
- Definition: Ongoing infusion of sterile solution
- Duration: Several hours to days
- System: Three-way catheter with irrigation port
- Rate: 30-60 mL/hour typically
- Indication: Post-surgical bleeding, clot prevention
Intermittent Bladder Irrigation (IBI)
- Definition: Periodic instillation of fluid
- Duration: As needed or scheduled
- System: Manual syringe or gravity system
- Volume: 30-60 mL per instillation
- Indication: Medication administration, debris removal
Memory Aids & Mnemonics
FLUSH Mnemonic for Indications
- Flush blood clots
- Lessen hematuria
- Unblock catheter obstruction
- Soothe bladder inflammation
- Heal post-surgical complications
MONITOR Mnemonic for Assessment
- Measure fluid balance
- Observe urine color/clarity
- Note vital signs
- Inspect catheter patency
- Test for pain/discomfort
- Order laboratory values
- Record intake/output
Comprehensive Nursing Care Plan Framework
Phase 1: Comprehensive Assessment
Physical Assessment
- • Vital signs (BP, HR, RR, Temp)
- • Abdominal examination
- • Bladder distension
- • Catheter insertion site
- • Skin integrity
Urine Characteristics
- • Color (clear, pink, red, dark)
- • Clarity (clear, cloudy, debris)
- • Odor (normal, foul, ammonia)
- • Volume output
- • Presence of clots
Laboratory Values
- • Hemoglobin/Hematocrit
- • Platelet count
- • Urinalysis
- • Electrolytes
- • Creatinine/BUN
Phase 2: NANDA Nursing Diagnoses
Primary Diagnoses
- Impaired Urinary Elimination related to bladder irrigation procedure
- Risk for Infection related to invasive procedure
- Acute Pain related to bladder distension
- Deficient Knowledge regarding procedure
Secondary Diagnoses
- Risk for Imbalanced Fluid Volume
- Anxiety related to procedure
- Risk for Injury related to catheter
- Disturbed Sleep Pattern
Phase 3: Planning & Goal Setting
SMART Goals for Bladder Irrigation
Short-term Goals (24-48 hours)
- • Patient will maintain patent catheter
- • Urine output will be >30 mL/hour
- • Pain level will be <4/10
- • Patient will verbalize understanding
Long-term Goals (Discharge)
- • Patient will be free from infection
- • Catheter will be discontinued safely
- • Patient will demonstrate self-care
- • Normal voiding pattern will resume
Phase 4: Implementation – Nursing Interventions
Independent Nursing Interventions
Catheter Care & Monitoring
- • Maintain sterile closed system
- • Monitor irrigation flow rate
- • Assess catheter patency hourly
- • Position drainage bag below bladder
- • Secure catheter to prevent tension
Fluid Balance Management
- • Calculate accurate intake/output
- • Monitor for fluid overload signs
- • Assess electrolyte balance
- • Document irrigation fluid volumes
- • Report significant imbalances
Collaborative Interventions
Medication Administration
- • Administer prescribed analgesics
- • Give antibiotics as ordered
- • Monitor for medication effects
- • Document medication responses
- • Report adverse reactions
Laboratory Monitoring
- • Monitor hemoglobin/hematocrit
- • Check electrolyte levels
- • Assess kidney function tests
- • Review urinalysis results
- • Report abnormal values
Monitoring & Complication Management
Continuous Monitoring Parameters
Vital Signs Monitoring
- • Blood pressure: Monitor for hypotension
- • Heart rate: Watch for tachycardia
- • Temperature: Assess for fever
- • Respiratory rate: Monitor for distress
- • Oxygen saturation: Maintain >95%
Urine Output Assessment
- • Minimum output: 30 mL/hour
- • Color progression: Dark → Pink → Clear
- • Clot presence: Large clots concerning
- • Flow rate: Continuous, not intermittent
- • Total volume: Match irrigation input
Potential Complications
Infection Risk
- • UTI symptoms: Fever, cloudy urine
- • Sepsis signs: Hypotension, confusion
- • Prevention: Sterile technique
- • Treatment: Antibiotics as prescribed
Fluid Imbalance
- • Overload: Edema, SOB, weight gain
- • Dehydration: Dry mucous membranes
- • Electrolyte shifts: Monitor Na+, K+
- • TURP syndrome: Hyponatremia
Catheter Complications
- • Blockage: Clots, debris obstruction
- • Displacement: Balloon deflation
- • Trauma: Urethral injury
- • Bladder spasms: Anticholinergics
Continuous Bladder Irrigation Procedure Flowchart
Documentation Requirements
Essential Documentation Elements
- Date & Time: All entries must be timestamped
- Irrigation Solution: Type, concentration, volume
- Flow Rate: mL/hour, adjustments made
- Urine Output: Color, clarity, volume, clots
- Patient Response: Comfort level, vital signs
- Complications: Any adverse events
- Interventions: Actions taken, effectiveness
Fluid Balance Calculation
Formula:
Actual Urine Output = Total Output – Irrigation Input
Example:
• Total drainage: 2000 mL
• Irrigation input: 1500 mL
• Actual urine: 500 mL
Patient & Family Education
Procedure Explanation
- • Purpose of irrigation
- • Duration expectations
- • Normal sensations
- • Importance of compliance
What to Expect
- • Feeling of bladder fullness
- • Urge to urinate
- • Pink-tinged urine initially
- • Gradual improvement
When to Call Nurse
- • Severe pain (>7/10)
- • No urine output
- • Fever/chills
- • Catheter displacement
Phase 5: Evaluation & Outcomes
Positive Outcomes Indicators
- • Clear or light pink urine
- • Adequate urine output (>30 mL/hr)
- • Absence of clots
- • Stable vital signs
- • Pain level <4/10
- • No signs of infection
- • Patient comfort maintained
Plan Revision Triggers
- • Goals not met within timeframe
- • New complications arise
- • Patient condition changes
- • Physician order modifications
- • Patient/family concerns
- • Equipment malfunction
- • Medication adjustments needed
Quality Improvement & Best Practices
Evidence-Based Practices
Infection Prevention
- • Maintain closed sterile system
- • Use aseptic technique for all procedures
- • Regular hand hygiene
- • Prompt catheter removal when appropriate
Patient Safety
- • Two-patient identifiers
- • Medication reconciliation
- • Fall prevention measures
- • Skin integrity maintenance
Interprofessional Collaboration
Team Communication
- • Regular physician updates
- • Nursing shift reports
- • Pharmacy consultations
- • Patient care conferences
Quality Metrics
- • Catheter-associated UTI rates
- • Length of stay
- • Patient satisfaction scores
- • Complication rates
Key Takeaways & Summary
CARE Principles for Success
- Continuous monitoring and assessment
- Aseptic technique maintenance
- Rapid response to complications
- Education and communication
Critical Success Factors
- • Thorough initial assessment
- • Appropriate nursing diagnoses
- • Evidence-based interventions
- • Continuous monitoring
- • Accurate documentation
- • Patient education
- • Interdisciplinary collaboration
Remember
Bladder irrigation is a complex nursing intervention that requires skilled assessment, continuous monitoring, and evidence-based care. Success depends on maintaining sterile technique, ensuring patient comfort, and recognizing complications early. Always prioritize patient safety and maintain clear communication with the healthcare team.
References & Further Reading
Clinical Guidelines
- 1. Cleveland Clinic. (2023). Continuous Bladder Irrigation: Purpose & Procedure. Retrieved from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/22597-continuous-bladder-irrigation
- 2. Agency for Clinical Innovation. (2023). Bladder irrigation: Management of haematuria. NSW Health.
- 3. Medical News Today. (2022). What to know about continuous bladder irrigation.
Professional Resources
- 4. American Nurses Association. (2023). Nursing Standards of Practice.
- 5. NANDA International. (2023). Nursing Diagnoses: Definitions and Classification.
- 6. The Joint Commission. (2023). National Patient Safety Goals.
