Therapeutic Approaches in Nursing
Art Therapy and Occupational Therapy
Comprehensive nursing notes featuring evidence-based information, visual aids, mnemonics, and flowcharts
Table of Contents
Art Therapy
Definition & Overview
Art therapy is a form of psychotherapy that uses art-making as a primary mode of expression and communication. It combines elements of visual arts, psychology, and therapy to improve or maintain mental health and emotional well-being.
Evidence Base
Research demonstrates that art therapy helps conditions relating to mood (anxiety, depression), trauma, low self-esteem, and cognitive decline. A 2024 meta-analysis revealed that art therapy significantly reduced anxiety levels (measured by SAS) among clinical nurses and healthcare professionals.
Benefits of Art Therapy
Psychological Benefits
- Reduces anxiety and depression symptoms
- Provides outlet for emotional expression
- Enhances self-awareness and insight
- Improves coping mechanisms
- Assists in trauma processing
Physiological Benefits
- Decreases stress hormones
- Reduces blood pressure
- Improves fine motor skills
- Enhances cognitive function
- Promotes mind-body connection
Mnemonic: “C-R-E-A-T-E”
Remember the core therapeutic elements of art therapy:
- Catharsis – Emotional release through artistic expression
- Reflection – Processing thoughts and feelings
- Expression – Communicating without words
- Awareness – Developing insight and self-understanding
- Transformation – Personal growth and change
- Empowerment – Building confidence and agency
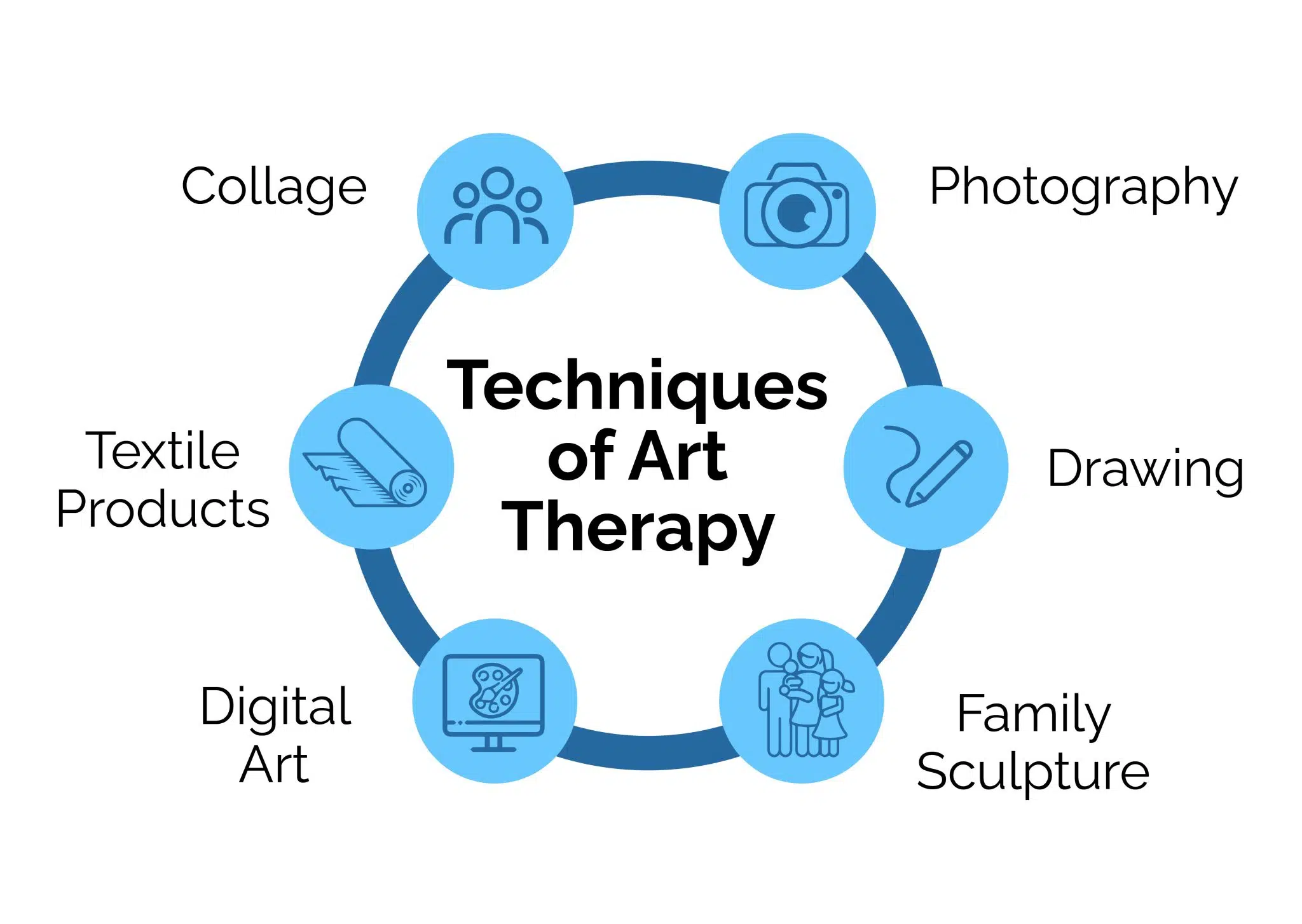
Art Therapy Process and Techniques
Visual Art Therapy
Visual art therapy uses drawing, painting, sculpture, and other visual media to express emotions, explore personal issues, and promote self-discovery. The focus is on the process of creation rather than the aesthetic outcome.
Common Techniques:
| Technique | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Free Drawing/Painting | Spontaneous expression without direction | Anxiety, emotional release, self-expression |
| Mandala Creation | Creating circular designs that promote focus | Anxiety reduction, mindfulness, centering |
| Collage Making | Arranging images and materials to convey meaning | Life review, goal setting, self-identity |
| Body Mapping | Drawing outline of body and marking emotions/sensations | Trauma, chronic pain, body image issues |
| Mask Making | Creating masks representing inner/outer self | Identity exploration, role conflicts |
Evidence in Nursing Practice
A 2023 study found that art therapy improved mental health outcomes in clinical nurses, with participants showing significant reduction in anxiety levels and reported improvements in job satisfaction. Another study demonstrated that art-making for 45 minutes significantly reduced cortisol levels in healthcare providers regardless of artistic experience.
Nursing Applications:
- Integrating simple art activities in patient assessments
- Offering art materials to patients experiencing anxiety or pain
- Using drawing to help patients express difficult emotions
- Collaborating with art therapists in treatment planning
- Utilizing art for self-care and preventing burnout
Dance/Movement Therapy (DMT)
Dance/Movement Therapy (DMT) is the psychotherapeutic use of movement to promote emotional, cognitive, physical, and social integration. It leverages the connection between movement and emotion to improve psychological and physical well-being.
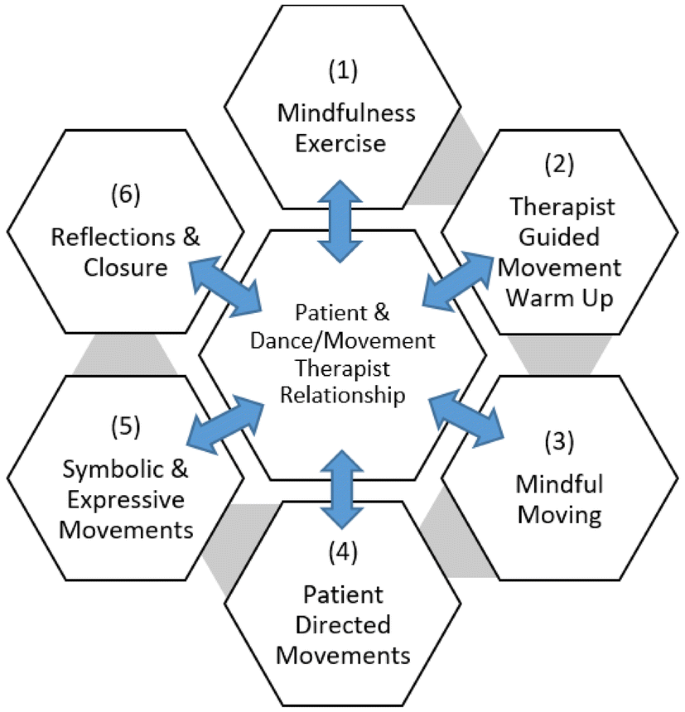
Medical Dance/Movement Therapy Framework
Key DMT Techniques:
Mirroring
Therapist or group members reflect a person’s movements to validate emotions and build empathy. Research shows mirroring activates mirror neurons, strengthening therapeutic connection.
Authentic Movement
Eyes-closed movement guided by inner sensations, with a witness observing. Helps develop body awareness, mindfulness, and integration of unconscious material.
Circle Formations
Group movement in circular patterns that promote community, safety, and shared experience. Particularly effective for social anxiety and isolation.
Movement Journeys
Guided imaginative movement sequences that explore emotional themes or life transitions through embodied expression.
Evidence Base
A 2019 systematic review found that DMT significantly improved quality of life, body image, and depression in various populations. UCLA Health research demonstrated that conscious or “ecstatic” dance helped reduce anxiety and depression symptoms, with participants showing improvement in mood regulation.
Dance Therapy and Nursing Integration:
- Implementing simple movement activities in psychiatric nursing
- Using gentle guided movements for pain management
- Incorporating rhythmic movement in rehabilitation settings
- Facilitating seated dance for elderly or limited-mobility patients
- Utilizing movement for nurse self-care and stress reduction
Mnemonic: “M-O-V-E-S”
Remember the therapeutic mechanisms of dance/movement therapy:
- Mindfulness – Present-moment body awareness
- Oxytocin release – Social bonding through movement
- Vitality – Increased energy and life force
- Embodiment – Connecting mind and body
- Self-expression – Communicating without words
Music Therapy
Music therapy is the clinical and evidence-based use of music interventions to accomplish individualized goals within a therapeutic relationship. It addresses physical, emotional, cognitive, and social needs through musical engagement.

Approaches in Music Therapy
Types of Music Therapy Interventions:
| Intervention Type | Description | Clinical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Receptive Music Therapy | Listening to music for relaxation, stimulation, or reflection | Pain management, anxiety reduction, sleep enhancement |
| Improvisational Music Therapy | Spontaneous creation of music using instruments or voice | Emotional expression, communication disorders, social skills |
| Compositional Music Therapy | Creating/writing songs or instrumental pieces | Grief processing, trauma recovery, identity exploration |
| Re-creative Music Therapy | Learning or performing pre-composed music | Cognitive rehabilitation, motor skills, confidence building |
| Rhythmic Entrainment | Using rhythm to stabilize physiological functions | Gait training, speech fluency, cardiac regulation |
Evidence in Nursing Practice
Research shows music therapy effectively addresses pain management (73.4%), coping (24.5%), stress reduction (22.3%), and anxiety reduction (15.5%) in hospital settings. A 2023 study demonstrated that nurse-implemented music interventions in community settings significantly reduced anxiety symptoms in people with severe mental illness.
Music Therapy Implementation Process
Music Therapy in Nursing Practice:
- Providing music for pain management during procedures
- Using personalized playlists for patients with dementia
- Incorporating rhythmic breathing with music for anxiety
- Facilitating group music experiences on psychiatric units
- Collaborating with music therapists on interdisciplinary teams
Important Considerations
When implementing music interventions, nurses should:
- Assess individual music preferences and cultural considerations
- Be aware of volume levels, especially for patients with sensory sensitivities
- Consider potential emotional reactions to certain music
- Understand the distinction between therapeutic music use and formal music therapy
- Follow facility protocols for music implementation
Occupational Therapy
Definition & Scope
Occupational therapy (OT) is a client-centered health profession concerned with promoting health and well-being through occupation. The primary goal is to enable people to participate in activities of everyday life that are meaningful and purposeful to them.

Scope of Occupational Therapy
Core Domains of Occupational Therapy:
Activities of Daily Living (ADLs)
- Self-care activities
- Bathing and hygiene
- Dressing
- Feeding
- Functional mobility
Instrumental ADLs (IADLs)
- Home management
- Meal preparation
- Financial management
- Medication management
- Community mobility
Participation Domains
- Work and education
- Play and leisure
- Social participation
- Rest and sleep
- Quality of life
Mnemonic: “O-C-C-U-P-A-T-I-O-N”
Remember the foundational principles of occupational therapy:
Occupational Therapy Process
According to the American Occupational Therapy Association (AOTA), the OT process consists of three main phases that guide practice:
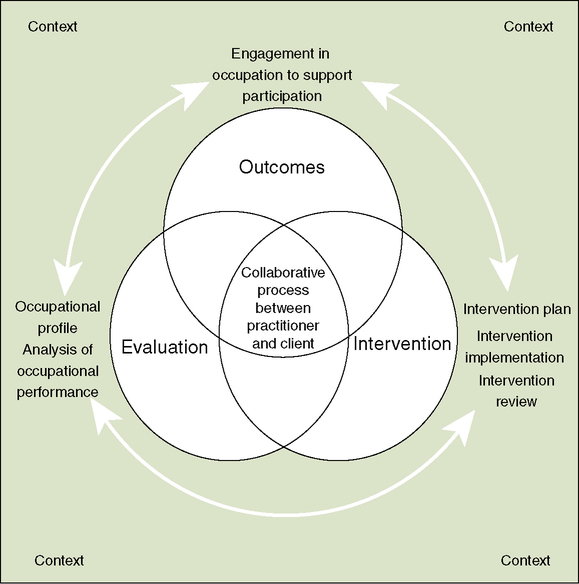
Occupational Therapy Process Framework
Occupational Therapy Process
1. Evaluation
Occupational profile & analysis of occupational performance
2. Intervention
Plan, implement, and review interventions to support participation
3. Outcomes
Measure results & determine next steps
Evaluation Phase:
Occupational Profile: Gathering information about the client’s occupational history, experiences, patterns of daily living, interests, values, and needs.
Analysis of Occupational Performance: Identifying factors that support or hinder performance in desired occupations, including body structures, body functions, habits, routines, roles, and environmental factors.
Intervention Phase:
Intervention Plan: Developing goals and selecting approaches based on theory, evidence, and client factors.
Intervention Implementation: Using occupations and activities, preparatory methods, education, training, advocacy, and group interventions.
Intervention Review: Continuous monitoring of client progress and modifying the approach as needed.
Outcomes Phase:
Outcome Measurement: Determining success in reaching goals and occupational performance improvement.
Discharge and Follow-up Planning: Creating plans for maintenance or transition to other services.
Interventions and Applications
Types of Occupational Therapy Interventions:
| Intervention Type | Description | Examples in Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Remediation/Restoration | Developing or improving skills and abilities | Fine motor exercises, cognitive retraining, strength training |
| Compensation/Adaptation | Modifying tasks or environments to support function | Adaptive equipment, environmental modifications, alternative techniques |
| Maintenance | Preserving capabilities and preventing decline | Energy conservation, joint protection, caregiver training |
| Prevention | Promoting health to prevent limitations | Fall prevention, ergonomic education, stress management |
| Health Promotion | Enhancing health, well-being and participation | Lifestyle redesign, wellness programs, community integration |
Evidence-Based Practice in OT
Research supports the effectiveness of occupational therapy interventions across various populations:
- Comprehensive OT programs reduce hospital readmissions for older adults by up to 30%
- OT interventions in schools improve handwriting legibility by an average of 42%
- Sensory integration approaches show moderate to strong effects for children with autism
- Home modifications and falls prevention programs reduce fall risk by 39%
- Cognitive rehabilitation improves daily function in individuals with traumatic brain injury
Clinical Applications by Setting:
Acute Care
- Early mobilization and self-care training
- Cognitive and functional assessments
- Discharge planning and equipment recommendations
- Patient/family education
Rehabilitation
- ADL/IADL training and retraining
- Therapeutic activities to improve function
- Environmental adaptations
- Community reintegration
Mental Health
- Life skills training
- Coping strategies development
- Group therapeutic activities
- Vocational rehabilitation
Pediatrics
- Sensory integration interventions
- Fine and gross motor skill development
- School-based accommodations
- Play-based therapy
Nursing and Occupational Therapy Collaboration:
Nurses and occupational therapists often work together to:
- Coordinate care for patients with complex needs
- Implement mobility and self-care protocols
- Address patient safety concerns
- Support discharge planning and transitions of care
- Provide education on medication management in daily routines
Important Distinctions
While nurses may incorporate some occupational therapy concepts, formal OT requires:
- Licensed occupational therapist or occupational therapy assistant
- Specialized assessment tools and intervention approaches
- In-depth knowledge of activity analysis and adaptation
- Understanding of occupational science principles
Nurses should collaborate with OT practitioners rather than replacing their specialized services.
Comparison of Therapeutic Approaches
Understanding the distinctions and overlaps between different therapeutic approaches helps nurses coordinate care and make appropriate referrals.
| Feature | Art Therapy | Dance/Movement Therapy | Music Therapy | Occupational Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Emotional expression & insight through visual art making | Integration of physical, emotional, and social aspects through movement | Using music to address physical, emotional, cognitive, and social needs | Enabling participation in meaningful daily activities |
| Theoretical Base | Psychotherapy, art psychology, creative expression | Movement analysis, somatic psychology, group dynamics | Neuroscience of music, psychology, auditory processing | Occupational science, rehabilitation, adaptation |
| Primary Goals | Self-expression, insight, emotional processing | Body awareness, emotional regulation, social connection | Emotional regulation, cognitive stimulation, pain management | Functional independence, participation in daily life |
| Assessment Focus | Symbolic content, creative process, emotional themes | Movement patterns, body awareness, interpersonal connection | Musical responsiveness, preferences, emotional reactions | Functional abilities, environmental factors, activity analysis |
| Role of Therapist | Guide the creative process and facilitate insight | Create movement experiences and reflect patterns | Facilitate musical engagement and therapeutic response | Analyze and adapt activities to enable participation |
Integration in Nursing Practice
When to Include Art Therapies
- Patients struggling with emotional expression
- When verbal communication is difficult
- For processing trauma or grief
- To enhance group cohesion in mental health settings
- For pain distraction and management
- To support cognitive stimulation
When to Include Occupational Therapy
- Difficulties with ADLs or IADLs
- Need for assistive devices or environmental modifications
- Cognitive rehabilitation needs
- Motor skill development or remediation
- Energy conservation and work simplification needs
- Community reintegration challenges
Evidence for Interdisciplinary Approaches
Research demonstrates improved outcomes when therapeutic approaches are integrated in care planning:
- Combined art therapy and occupational therapy interventions show enhanced outcomes for patients with traumatic brain injuries
- Integrating music therapy with traditional rehabilitation improves motor recovery in stroke patients
- Dance/movement therapy complements occupational therapy in improving balance and coordination in older adults
- Interdisciplinary teams that include multiple therapy modalities report higher patient satisfaction and engagement
Case Study: Integrating Therapeutic Approaches
Patient: 72-year-old female with right-sided weakness following stroke
Comprehensive Care Plan:
Occupational Therapy Focus:
- ADL retraining with adaptive equipment
- Home safety evaluation and modifications
- Upper extremity exercises for functional use
- Cognitive assessment and strategies
Art Therapy Focus:
- Painting with non-dominant hand to address frustration
- Visual expression of emotional adjustment to disability
- Group art activities for social reintegration
Dance/Movement Therapy Focus:
- Seated dance activities for balance and coordination
- Rhythmic movement patterns to reinforce gait
- Body awareness exercises for spatial orientation
Music Therapy Focus:
- Rhythmic auditory stimulation for gait training
- Instrument playing for fine motor coordination
- Music listening for mood elevation and motivation
Nursing Role in Integration:
- Coordinate scheduling of therapeutic activities
- Reinforce therapeutic techniques during daily care
- Monitor fatigue levels and emotional responses
- Document observations regarding function and participation
- Communicate progress and challenges to therapy team
Key Takeaways
Art Therapy Principles
- Uses creative expression to promote healing and well-being
- Includes visual arts, dance/movement, and music modalities
- Effective for emotional expression, particularly when verbal communication is difficult
- Evidence supports benefits for anxiety, depression, and trauma
- Nurses can incorporate elements while collaborating with specialists
- Remember “C-R-E-A-T-E” framework for therapeutic elements
Occupational Therapy Principles
- Focuses on enabling participation in meaningful daily activities
- Addresses ADLs, IADLs, and broader participation in life
- Process includes evaluation, intervention, and outcomes
- Utilizes remediation, compensation, and prevention approaches
- Evidence supports effectiveness across various populations
- Remember “O-C-C-U-P-A-T-I-O-N” framework for core principles
Nursing Integration Framework
As a nurse, remember these principles when incorporating therapeutic approaches:
Collaborate
Work with specialists rather than replacing them
Reinforce
Support therapy goals in daily nursing care
Observe
Monitor responses and document effectiveness
Educate
Help patients understand therapeutic benefits
References
- American Occupational Therapy Association. (2020). Occupational therapy practice framework: Domain and process (4th ed.). American Journal of Occupational Therapy, 74(Suppl. 2).
- American Art Therapy Association. (2022). About art therapy. https://arttherapy.org/about-art-therapy/
- American Music Therapy Association. (2023). What is music therapy? https://www.musictherapy.org/about/musictherapy/
- American Dance Therapy Association. (2023). FAQ. https://www.adta.org/FAQ
- Cleveland Clinic. (2023). Music therapy: Types & benefits. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/8817-music-therapy
- Klammer, S. (2023). Art: A healing tool for nurses. American Nurse Journal. https://www.myamericannurse.com/art-a-healing-tool-for-nurses/
- Koch, S. C., Riege, R. F., Tisborn, K., Biondo, J., Martin, L., & Beelmann, A. (2019). Effects of dance movement therapy and dance on health-related psychological outcomes. A meta-analysis update. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 1806.
- National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. (2023). Music and health: What you need to know. https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/music-and-health-what-you-need-to-know
- World Federation of Occupational Therapists. (2023). About occupational therapy. https://wfot.org/about/about-occupational-therapy
- Zubala, A., & Karkou, V. (2018). Arts therapies in the treatment of depression. London: Routledge.
